Features
Our institutional repositories (IR) are organized to accommodate the multidisciplinary and organizational needs of a large institution. They are organized into Communities, Sub-Communities, and Collections, each of which can be customized to allow for flexibility in determining policies and workflow.
The IRs use an open-source DSpace software, originally developed by MIT and Hewlett Packard. DSpace provides the stable, long-term storage needed to house the digital products of UHM faculty and researchers.
The Structure
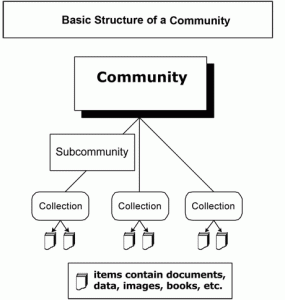
The IRs are made up of Communities, Sub-communities, and Collections.
Communities are groups that contribute content to the repository. These might be departments, labs, research centers, schools, or other administrative units within an institution. Communities determine their own content guidelines and decide who has access to its contributions. A library staff member works with the head of a Community to set up workflows for content to be approved, edited, tagged with metadata, etc.
Communities can be further divided into Sub-communities to reflect an organizational structure, or to group certain collections together.
Collections, house the individual content items or files. A collection belongs to one community, but items may be mapped between collections; For example, a research collaboration between two communities may result in an item belonging to a different collection in each of the communities.
Access Control
The IRs allow contributors to limit access to at the collection and the individual item level. However, all contributions must follow UHM’s Access Policy.
Search & Retrieval
The submission process allows for the description of each item using a qualified version of the Dublin Core metadata schema. Descriptions are entered into a relational database, which is used by the search engine to retrieve items.
Digital Preservation
- The IRs provide long-term physical storage and management of digital items in a secure, professionally managed repository including standard operating procedures such as backup, mirroring, refreshing media, and disaster recovery.
- The IRs assign a persistent identifier to each contributed item to ensure it is retrievable far into the future.
- The IRs provide a mechanism for advising content contributors of the preservation support levels they can expect for the files they submit.
Supported Digital Formats & Content Types
The IRs accept all manner of content in a variety of digital formats. Some examples are:
- Documents, such as articles, preprints, working papers, technical reports, conference papers
- Books
- Theses and dissertations
- Data sets
- Computer programs
- Visualizations, simulations, and other models
- Multimedia publications
- Bibliographic datasets
- Images
- Audio files
- Video files
- Learning objects
- Web pages
The DSpace Platform
The IRs run on DSpace. Developed jointly by the MIT Libraries and Hewlett-Packard Company, DSpace is an open source software platform for building digital repositories.
The DSpace open source platform is freely available at GitHub. Institutions around the world use DSpace to store their digital research materials – see which institutions are running DSpace services.
DSpace has an active developer community, with a variety of online resources:
Technical Support
The UHM Library runs and maintains the repository servers for all UH Communities. Communities do not have to download the system or maintain any servers. Users use a web-based interface to save, search, and store their data.

